0 Latitude Is Called The
Latitude lines start at the equator (0 degrees latitude) and run east and west, parallel to the equator. Lines of breadth are measured in degrees northward or south of the equator to xc degrees at the North or Due south poles. A transcript is available that describes this infographic content in plain text. (Image credit: iStock)
Lines of latitude, also chosen parallels, are imaginary lines that divide the Earth. They run east to due west, merely measure your distance north or south. The equator is the most well known parallel. At 0 degrees latitude, it equally divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. From the equator, latitude increases equally you travel n or due south, reaching 90 degrees at each pole.

Since 1899
Did you know that the National Ocean Service (NOS) has been monitoring latitude since 1899? A scientist with the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey (afterward incorporated into NOS) built an observatory near his home in Gaithersburg, Maryland, and began collecting latitude measurements equally role of a global project to monitor the wobble of the Earth on its polar axis. Some other observatory was built in Ukiah, California, joining international stations at locations along the 39th parallel due north. Satellite data replaced homo observations in the 1980s, but the data from the observatories is withal being used.
In that location are other named lines of breadth. They're based on the lord's day'south position during Earth's orbit, and they help the states understand climate, weather, and ocean currents. The Tropic of Cancer, at roughly 23 degrees north, and the Tropic of Capricorn, at roughly 23 degrees due south, are the boundaries of what we consider the tropics. The Arctic Circle and the Antarctic Circle are at roughly 66 degrees north and s, respectively. They mark the boundaries of the Arctic and Antarctic regions.
Each degree of latitude covers about 111 kilometers on the Globe's surface. I caste of breadth can be further divided into 60 minutes, and one minute tin be farther divided into 60 seconds. A 2nd of latitude covers just about 30.7 meters. Unlike longitude lines, which get closer to each other at the poles, latitude lines are parallel. No affair where you are on Earth, latitude lines are the same distance autonomously.
Latitude and longitude take been used in astronomy and navigation since ancient times. By calculating the angle between the horizon and a celestial object (usually the sun or the North Star), navigators could determine their approximate latitude using basic tools. The calculations were simple, then measuring latitude at ocean was reliable hundreds of years before accurate longitude measurements could exist calculated during a voyage. If the North Star was 60 degrees above the horizon, the observer was at 60 degrees breadth (n). This process was more than complex in the southern hemisphere, where the North Star is not visible.
We still expect to the sky to determine our position, simply the equipment is a bit more sophisticated. A constellation of over thirty global positioning satellites orbit the Globe, transmitting signals to receivers on land. NOS'due south National Geodetic Survey manages a network of stationary global positioning satellite receivers called Continuously Operating Reference Stations (CORS). When combined with other positioning data in the National Spatial Reference System, processed CORS data can provide latitude, longitude, and summit positions authentic to within a few centimeters.
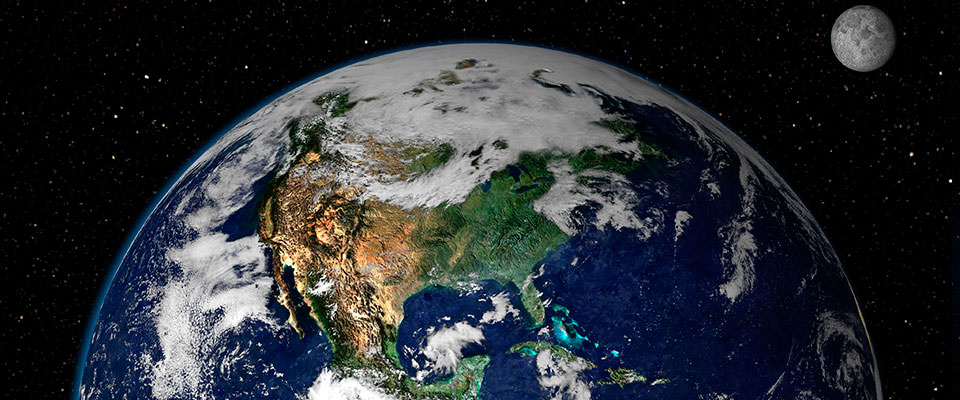

While the Earth appears to be round when viewed from the vantage point of infinite, it is really closer to an ellipsoid. Our planet is pudgier at the equator than at the poles due to the centrifugal force created past the world's constant rotation. The fact that the World is non a perfect sphere makes calculating latitude lines with high degrees of accuracy a complicated endeavor.
Degrees of Accurateness
If we assume the Earth is a perfect sphere, lines of breadth are relatively simple to calculate. The latitude of a sure point on the surface of the World is the angle between two lines: a line from that location to the center of the Earth and a line from the heart of the Earth to the Equator. This method of calculation gives us geocentric lines of latitude. However, this method is not accurate enough for astronomy, global positioning, and other existent-world applications. Instead, nosotros use what is known equally geodetic latitude. This method of calculating latitude for any indicate on Earth accounts for the fact that the Earth is actually squished at the poles due to the centrifugal force created past the planet's rotation. Measuring latitude lines with high degrees of accuracy is only one component of geodesy, the scientific discipline of accurately measuring and understanding the Earth's geometric shape, orientation in space, and gravity field.
Infographic Transcript: Breadth
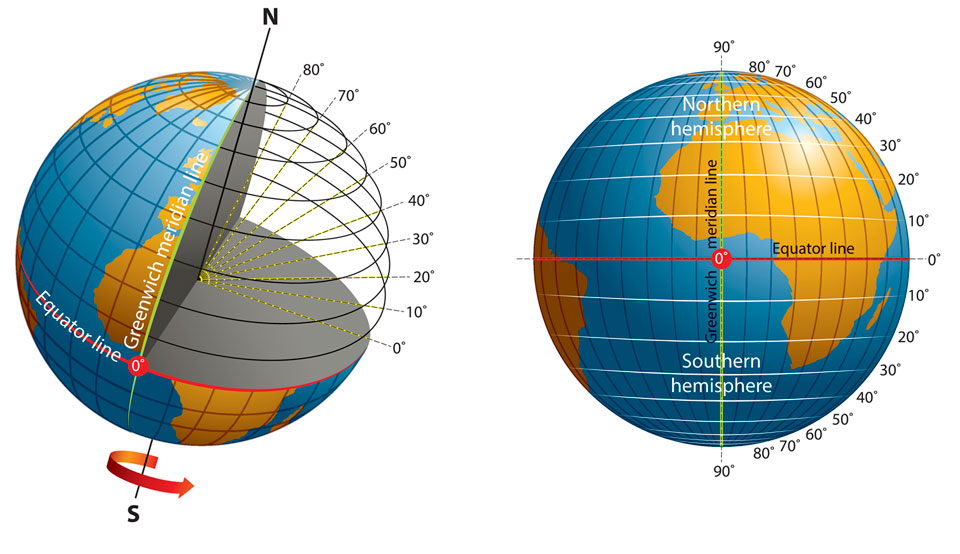
- The left paradigm shows the Globe tilted on its centrality. A section has been cut away to evidence breadth lines (or parallels) that run horizontally from the equator to the Due north Pole. These are labeled from 0 to 80 degrees north. The equator and the Greenwich acme line (prime meridian) are also labeled. Additional lines are fatigued from the center of the Globe to each labeled parallel. These illustrate that the latitude measurement for each bespeak equals the angle made between the line to the center of the world and one drawn through the plane of the equator. Most the Due south Pole, an arrow indicates the direction of the Earth's rotation on its axis.
- The right prototype shows the Earth with the equator and Greenwich meridian line labeled. The expanse n of the equator is labeled Northern Hemisphere; the area south of the equator is labeled Southern Hemisphere. Breadth lines are labeled from the north pole (xc degrees north) to the equator (0 degrees) and downwards to the south pole (90 degrees s).
0 Latitude Is Called The,
Source: https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/latitude.html
Posted by: robinsonweir1970.blogspot.com


0 Response to "0 Latitude Is Called The"
Post a Comment