Is Dna Soluble In Alcohol
"The function of alcohol in DNA extraction is to precipitate, launder and store DNA. Let's find out how it executes each part."
Liquid-liquid Dna extraction highly relies on various chemical combinations and solutions. Lysis buffer, an utmost requirement of Deoxyribonucleic acid extraction, is needed to lyse cells. The buffer here contains many ingredients that assistance in the extraction process.
In the next step, the liquid nucleic acrid extract is precipitated and eluted and stored. The classic Maniatis and Sambrook protocol uses this principle to extract Deoxyribonucleic acid. Here booze performs crucial functions.
Precipitates of Deoxyribonucleic acid are visible, the cotton fiber-treat-like construction appears after booze treatment. But how does it occur? In addition, how other two functions are executed and what is the type of alcohol used for precipitation, washing and storing Dna?
This article is a practical guide and a part of Dna extraction. We will sympathise the part of alcohols- isopropanol, ethanol and methanol in Dna extraction.
"Reaction betwixt solute and solvent creates an insoluble solid substance, called a precipitate and the process is referred to as precipitation."
Stay tuned.
What is the function of alcohol in DNA extraction?
Alcohol performs three different functions in Deoxyribonucleic acid extraction, which are precipitation washing and storing.
Dna atmospheric precipitation:
To improve understand the present mechanism, let'south beginning with some basics and groundwork information. Two phenomena of polarity and dielectric constant are important to discuss here.
Polar and nonpolar molecules dissolve in polar and nonpolar solutions, respectively. Solute and solvents dissolve properly only if they have a similar construction. Dna is a polar molecule and soluble in h2o every bit water is also partially polar.
Chemically water has a partial negative charge near the oxygen atom and a partial positive accuse near the hydrogen cantlet. The negatively charged phosphate backbone of Dna interacts with the positive accuse of water.
This interaction dissolves DNA in water and stabilizes its structure. Technically it's the electrostatic interaction betwixt the H+ of water and POiii – of the Deoxyribonucleic acid.
In addition to this, DNA is likewise a hydrophilic molecule (Hydro means water and philic means to attract) which literally means, it attracts h2o and solubilizes. But that's non the case with alcohol.
When we add alcohol and salt, DNA precipitates into a visible form. So what exactly happens there? Now precipitation can exist explained by the dielectric constant of water and alcohol.
According to Coulomb's law, "force of allure betwixt ii opposite charges is inversely proportional to the dielectric abiding." The dielectric constant of water is ~lxxx and alcohol is 24.
Equally per the law, alcohol repeals Dna stability.
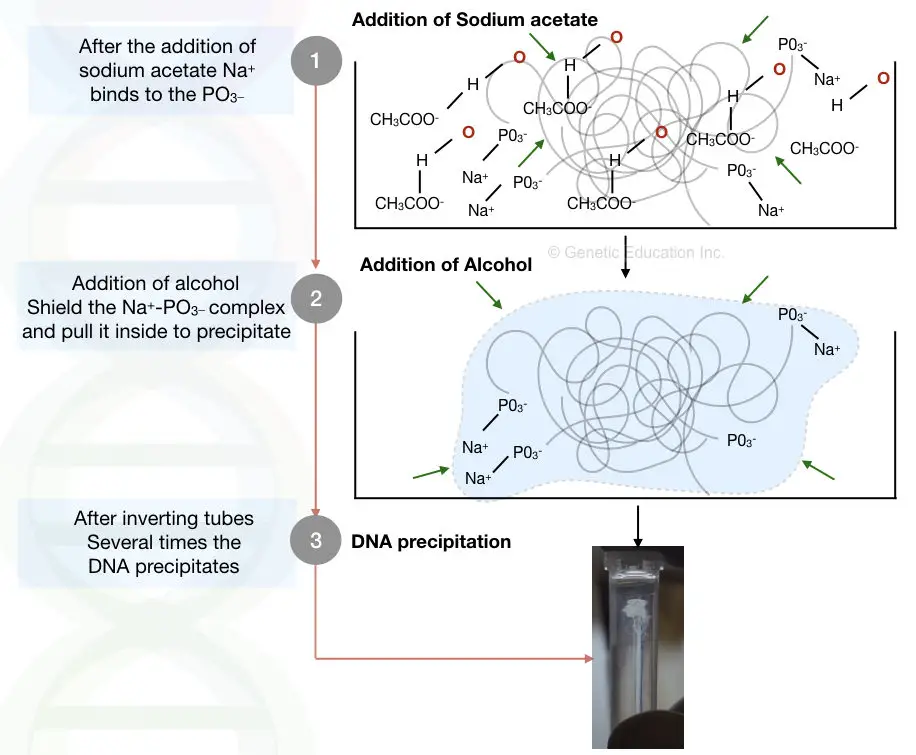
When we add salt for let's say sodium acetate (CH3COONa+). The positively charged Na+ reacts with the negatively charged phosphate of the DNA. Now this reaction makes Deoxyribonucleic acid less hydrophilic.
Only water can destroy everything, the positive charge of water will try to dissolve and stabilize it. When nosotros add together alcohol, the net negative charge of alcohol makes the positive charge of water busy.
This disallows h2o to collaborate with the Deoxyribonucleic acid. pregnant, that alcohol prevents the Na and POiii – complex by neutralizing other positive charges. When we add more and more alcohol it neutralizes as many positive charges as possible from the solution and precipitates Dna in a visible class.
By the addition of a double volume of alcohol, almost all positive charges of water are neutralized by alcohol which pulls DNA out from the solution and eventually nosotros tin can see a visible precipitate of DNA.
Normally, a doubled volume of isopropanol is used for atmospheric precipitation in combination with sodium acetate salt. Ethanol tin can also be used. Do you know how precipitation occurs? Check out this commodity: A Quick Guide on DNA Precipitation and Protocol.
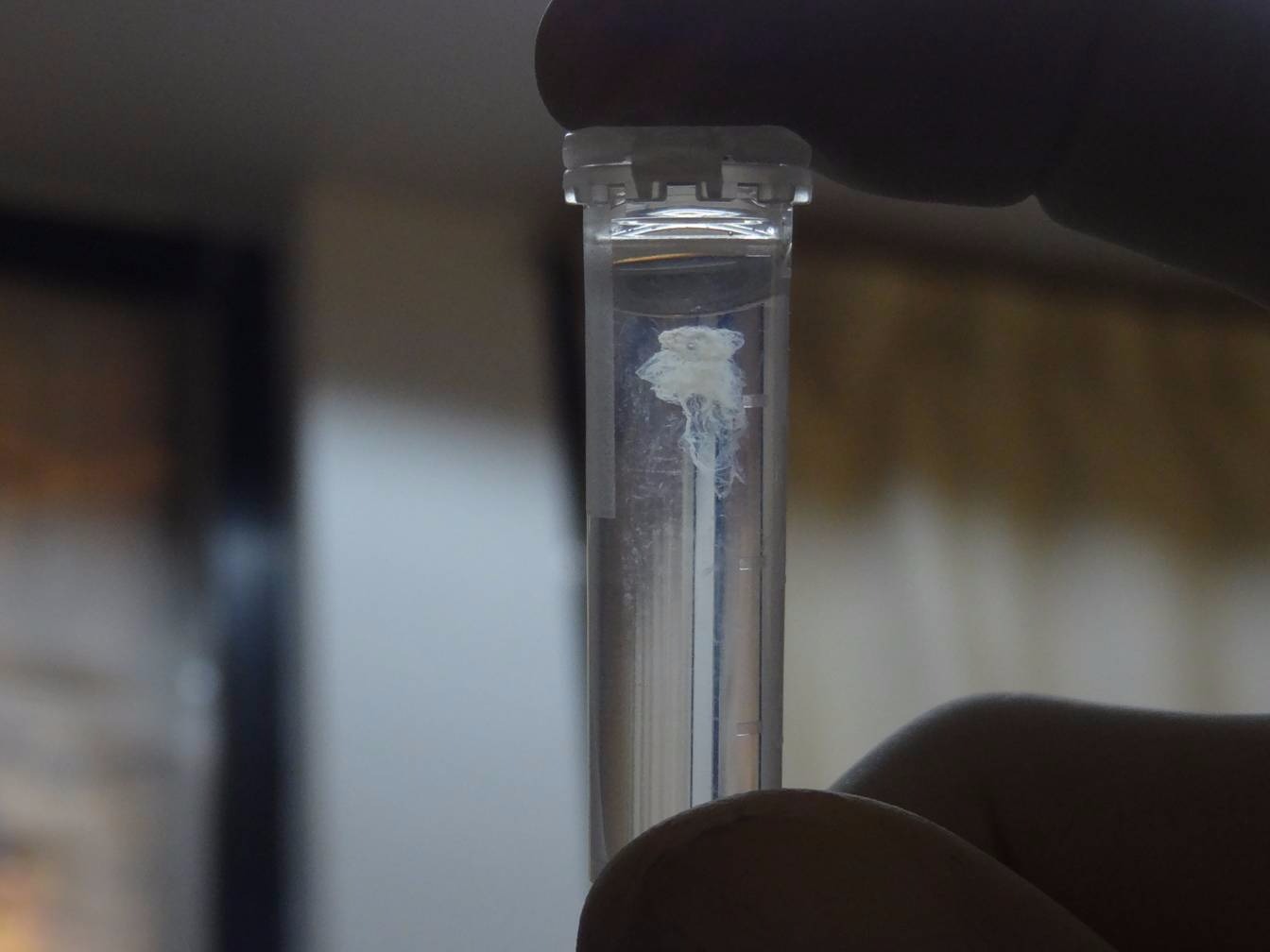

The actual epitome of DNA precipitate. ©Genetic Teaching Inc.
Dna washing:
Alcohol cleans DNA and removes other contaminants. Once once more information technology uses the same principle. When we launder Deoxyribonucleic acid with alcohol (by gently inverting the tube many times), alcohol passes through the DNA and removes proteins, salts and traces of other chemicals.
Centrifugation will remove the contaminants and by doing air-drying alcohol can be evaporated besides.
Usually, 70% ethanol is recommended to wash DNA precipitates. 3-fourth dimension washing is appropriate at 10,000 rpm centrifugation.
DNA storing:
TE dissolves Deoxyribonucleic acid but over a period dissolved DNA tin exist degraded to some extent and sometimes, lose its properties. Adding alcohol to precipitate volition make precipitate intact, foreclose solubilization and thereby deposition.
1 to i.5ml of ethanol (70%) is added to pellets and stored at -20°C temperature for years. The Dna volition remain safety.
Which booze to use for Deoxyribonucleic acid precipitation?
Now the experts part comes. You may wonder which alcohol from the isopropanol, ethanol and methanol. Here is the answer.
I personally do not recommend methanol. Information technology is simply an option you can consider but not useful. A doubled volume of ethanol and a single volume of isopropanol is used for precipitation. Notably, both should be 100% (absolute).
So the advantage of using isopropanol over ethanol is the low-volume requirement of the isopropanol. However, isopropanol can pro-precipitate more salts and also creates difficulties in DNA drying.
Technically, for 1 ml nucleic acrid extract, you need 2 to 2.v ml ethanol and 0.6 to 1 ml isopropanol.
| Alcohol | Concentration | Function |
| Isopropanol | 100% (Pure) | Dna Atmospheric precipitation |
| Ethanol | 100% and lxx% | Dna atmospheric precipitation and Deoxyribonucleic acid washing |
| Ethanol | seventy% | DNA storage |
| Methanol | 70% | Dna washing |
Wrapping up:
These are iii of import functions of booze in DNA extraction. Precipitation is an of import step here. The unabridged success of the experiment depends on how keenly you precipitated and washed Dna.
My technical noesis also supports that chilled booze increases the yield of the precipitate. It is advisable to store isopropanol at -20°C earlier use and apply it in chilled class. Lower temperature prevents enzymatic degradation of Deoxyribonucleic acid and thus nosotros become high pure and high yield Dna.
FAQs:
Is Dna Soluble In Alcohol,
Source: https://geneticeducation.co.in/what-is-the-role-of-alcohol-in-dna-extraction/
Posted by: robinsonweir1970.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Is Dna Soluble In Alcohol"
Post a Comment